|
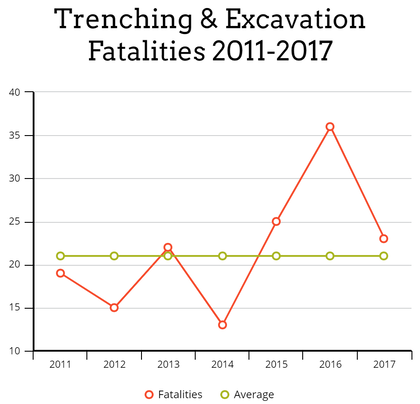
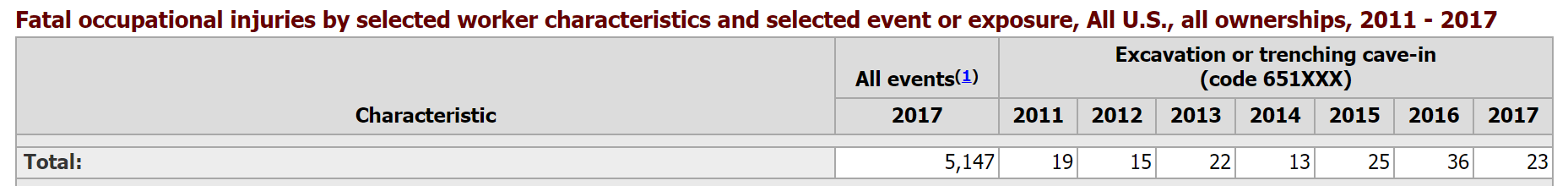
Trenching & Excavation Safety Information: According to the Bureau of Labor during a 7 year stretch between 2011-2017 153 people were killed in a trench or excavation accident. That's on average 21 people per year in that time period. That's 153 families that have lost a loved one that they will never see again. The first alarming trend, is that trenching and excavation fatalities have been on an upward trend after hitting an all time low of 13 back in 2014. The second alarming trend is the size of company that a majority of these fatalities are from companies with fewer than 50 workers. 68% of those fatalities occurred in companies with fewer than 50 workers. 46% of the deaths occurred in small companies with 10 or fewer workers. Training employees in trenching and excavation safety hazards, protective systems, and role of the competent person is crucial in prevention further fatalities and injuries. What is the different between a Trench and an Excavation?
OSHA defines an excavation as any man-made cut, cavity, trench, or depression in the earth’s surface formed by earth removal. A trench is defined as a narrow underground excavation that is deeper than it is wide and is no wider than 15 feet (4.5 meters). Dangers of Trenching and Excavation
Access and Egress OSHA requires safe access and egress to all excavations, including ladders, steps, ramps, or other safe means of exit for employees working in trench excavations 4 feet (1.22 meters) or deeper. These devices must be located within 25 feet (7.6 meters) of all workers. Protect Yourself Do not enter an unprotected trench! Trenches 5 feet (1.5 meters) deep or greater require a protective system unless the excavation is made entirely in stable rock. Trenches 20 feet (6.1 meters) deep or greater require that the protective system be designed by a registered professional engineer or be based on tabulated data prepared and/or approved by a registered professional engineer. Ensure that spoil piles are at least 2 feet away from the edge of the trench or excavation. Protective Systems There are different types of protective systems:
Inspections & Competent Person OSHA standards require that trenches be inspected daily or at the start of each shift and as conditions change (such as after a rainstorm) by a competent person prior to worker entry to ensure elimination of excavation hazards. A competent person is an individual who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards or working conditions that are hazardous, unsanitary, or dangerous to employees and who is authorized to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate or control these hazards and conditions.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSTAC Admin Categories
All
Archives
July 2024
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed