|
OSHA Standard: 1926.64
Training Requirement: Initial training is required for each employee involved in operating a process of highly hazardous chemicals BEFORE being involved in that operation. Refresher training shall be provided at least every three years, and more often if necessary. Training Documentation: The employer shall prepare a record which contains the identity of the employee, the date of training, and the means used to verify that the employee understood the training. Training: All employees, including maintenance and contractor employees, involved with highly hazardous chemicals need to fully understand the safety and health hazards of the chemicals and processes they work with for the protection of themselves and others. The operating procedures are often viewed as the standard operating practices (SOPs) for operations. Control room personnel and operating staff, in general, need to have a full understanding of operating procedures. Training in subjects such as operating procedures and safety work practices, emergency evacuation and response, safety procedures, routine and nonroutine work authorization activities, and other areas pertinent to process safety and health will need to be covered by an employer’s training program. Because of this this, hands-on-training is strongly encouraged to be used. Training evaluations are strongly encouraged. If, after the evaluation, it appears that the trained employees are not at the level of knowledge and skill that was expected, the employer will need to revise the training program, provide retraining, or provide more frequent refresher training sessions until the deficiency is resolved. Audits: Employers need to select a trained individual or assemble a trained team of people to audit the process safety management system and program. The audit is to include an evaluation of the design and effectiveness of the process safety management system and a field inspection of the safety and health conditions and practices to verify that the employer’s systems are effectively implemented. Evaluate: Employers need to periodically evaluate their training programs to see if the necessary skills, knowledge, and routines are being properly understood and implemented by their trained employees. OSHA Standard: 1926.62
Frequency of Training: Upon initial assignment and annually thereafter, or more frequently depending on change in policy, assignment, and tools used. Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL): 50 micrograms of lead per cubic meter of air, as averaged over an 8-hour period. Background: Lead (Pb) is a heavy metal that can threaten the health of workers in many occupations. Lead can be inhaled or swallowed and once inside the body tends to remain in tissue and organs. Eventually, after repeated exposures, lead build-up becomes toxic. Exposure to lead fumes and particles can come from many sources, including abrasive blasting, sanding, torch cutting, scraping, and loosening old paint with a propane torch. Dust and fumes can be inhaled, including by family members shaking out clothes. Lead can also get into the body by being transferred from dirty hands to food and drink. Serious damage can occur to your lungs, brain, liver and other organs. Children are particularly at risk for lead dust brought home from the job. How You Can Protect Yourself Lead exposure can be maintained at acceptable levels if the following practices are followed: Use an exhaust ventilation system where provided. Use a respirator that will properly protect you. Keep the worksite clean. Use only a vacuum with a HEPA filter or wet cleaning methods when removing lead dust. Never use compressed air for cleaning. Eat, drink, or smoke in areas away from the worksite. Keep all lunch boxes and coffee cups away from the work area. Use protective clothing. Store street clothes separate from work clothes. Never wear contaminated clothing home. Employer Responsibilities:
In an age dominated by technology and the internet, only 18% of companies consider themselves paperless. In fact, nearly a third of companies are buying more paper than they were 5 years ago. Businesses in the United States spend $8 billion annually on managing paper. Workers are spending up to half of their time looking for paper information each year. 41% of HR personnel spend over 10 minutes a day searching for the documents and information they need to carry out their jobs. Of these, half spend more than 20 minutes! Lucky, STAC is one of the few companies offering a solution, going digital.
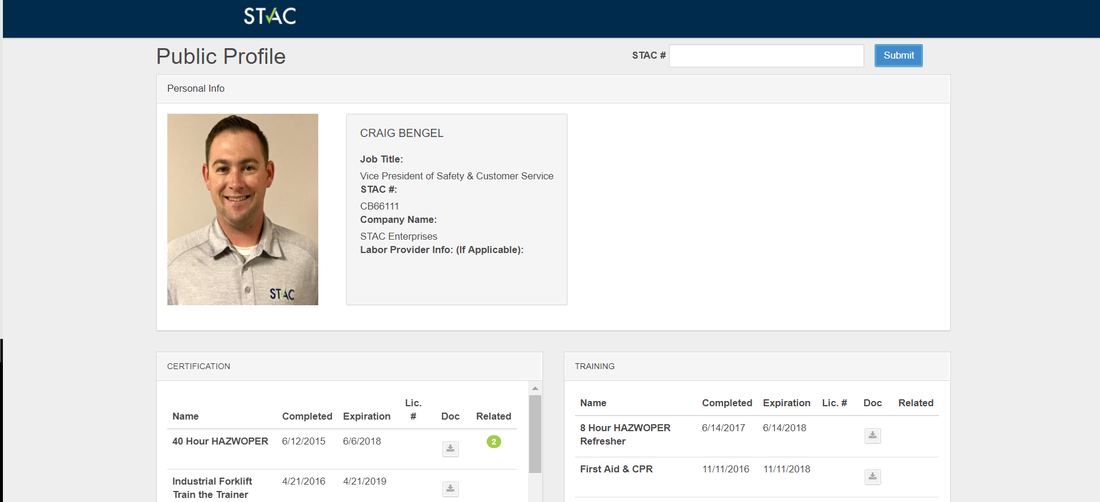
The STAC system offers a central location for all employee information: training, personnel information, drug test, emergency contact information, employee reviews, clothing sizes, etc. Here are some specific benefits to better organization through digital records: 1) Cost Savings: Simply switching to digital records could save a company upwards of $325,000 in 10 years from cost and materials. 2) Space Savings: Think about the space you are currently using for paper records; do you think that is going to get any smaller in the future? 3) Disaster Proof: A digital cloud based profile is immune to disasters such as hurricane, fire, or flood that could destroy paper records forever. 4) Security Protection: Filing cabinets not locked, files left in the wrong spot or left on the printer makes employee information vulnerable. Digital records provide a secure access and ease of mind. 5) Easily Searchable: Instead of shifting through paper records, an employee could simply go to a profile and quickly search through for the documentation. 6) Easily Shareable: Easily share the information with other people as needed without having to copy anything. 7) Ease of Use: Employees are working on the go more than ever. Don’t have them tied down to paper records stuck at the office. |
AuthorSTAC Admin Categories
All
Archives
July 2024
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed