|
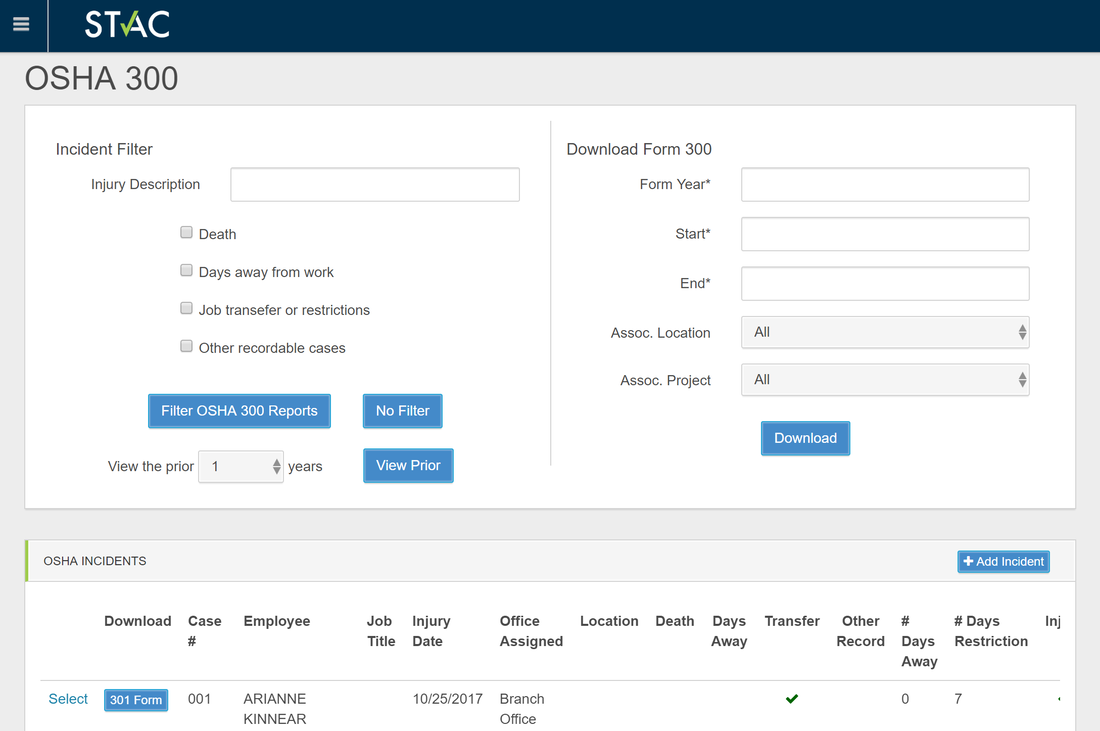
One simple information input will automatically create and update the OSHA 300, 300A, and 301 forms. Within the system there is the ability to filter between type of injury and year. Whenever necessary or at least annually, download the summary to the correct OSHA format for printing and displaying with the office or jobsite and submit to OSHA.
0 Comments
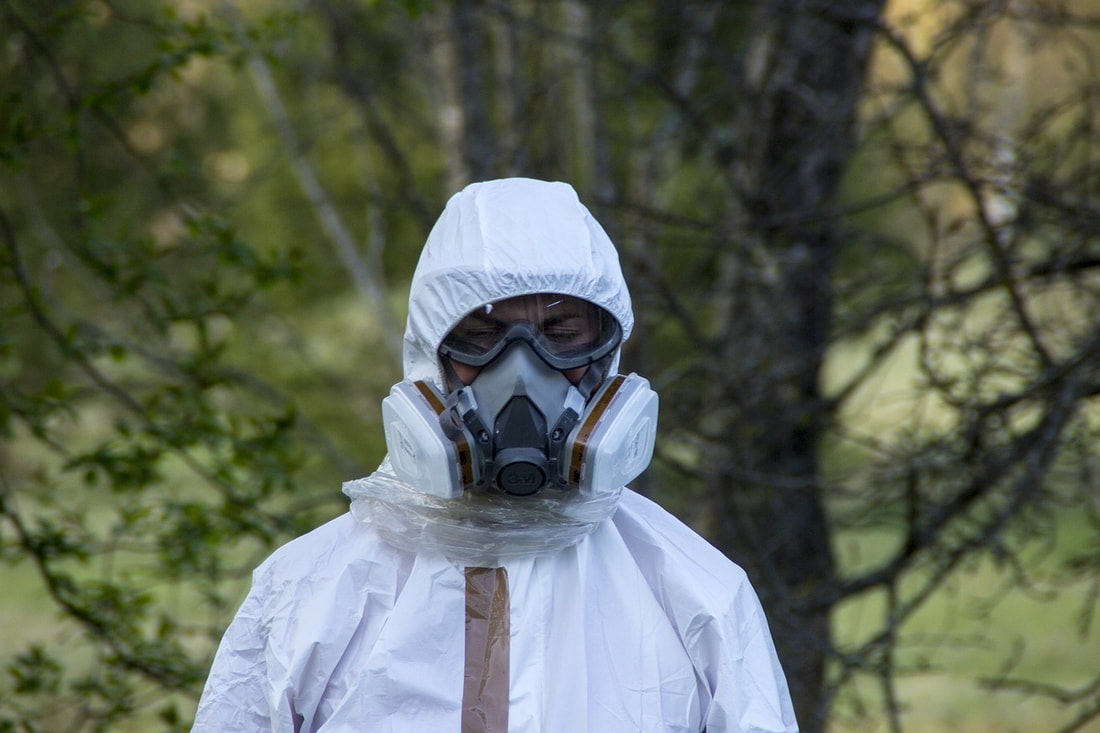
OSHA Standard: 1910.134 Training Frequency: Upon initial assignment (before mask is worn), and annually. Training Style: Hands-on When is Respiratory Protection Required? - In any workplace where respirators are necessary to protect the health of the employee or whenever respirators are required by the employer Background: Respiratory Protection Program: Respiratory protection program requires the employer to develop and implement a written respiratory protection program with required worksite-specific procedures and elements for required respirator use. The program must be administered by a suitably trained program administrator. In addition, certain program elements may be required for voluntary use to prevent potential hazards associated with the use of the respirator. The program shall be updated as necessary to reflect those changes in workplace conditions that affect respirator use. The employer shall include in the program the following provisions:
The employer shall provide respirators, training, and medical evaluations at no cost to the employee. Training Information: The training must be comprehensive, understandable, and recur annually, and more often if necessary. The employer shall ensure that each employee can demonstrate knowledge of at least the following:
Retraining: Retraining shall be administered annually, and when the following situations occur:
OSHA Standard: 1926.102
Training: Initially Upon assignment and as conditions or equipment changes The employer shall train each affected employee:
Protectors shall meet the following minimum requirements:
Eye and face protection equipment required by this Part shall meet the requirements specified in American National Standards Institute, Z87.1-1968, Practice for Occupational and Educational Eye and Face Protection.
|
AuthorSTAC Admin Categories
All
Archives
July 2024
|





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed