|
In July 2023, OSHA created a National Emphasis Program on Warehouse and Distribution Centers to evaluate high-risk workplaces. Since this program was enacted, over 600 inspections have been conducted by OSHA with nearly $2.5 million in penalties, most of which involve Powered Industrial Trucks (PIT). Below we will focus on the operation and training procedures of PITs and some hazards to be aware of when in use.
PIT Operation Before operating a PIT some things to remember:
PIT Training Requirements Before operating PITs, you need to be trained by a competent person. Training requirements include:
When it comes to PIT use in and around your workplace, making sure you have been properly trained is paramount to the safety of yourself and your coworkers. To keep the conversation going, download the Forklift Safety Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below.
0 Comments
Recently OSHA updated the Hazard Communication (HAZCOM) Standard which controls the rules on how to handle potentially harmful chemicals in the workplace. Effective on July 19th, the intent of the updated standard is to align with international trade partners and make things easier for manufacturers and distributors to transport chemicals. Let's dive into some of the updates to the standard and refresh employers on their responsibilities regarding hazardous chemicals.
What’s New Some of the major changes found between the 2012 and 2024 standards include:
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/HCS_side-by-side.pdf Employer Responsibilities
Why Does This Matter to You About 3,500 workers are injured and another 1,000 die each week from exposure to hazardous substances and from not understanding the proper protocols in case of a spill or exposure. These updates will assist in providing more information to anyone distributing or working with hazardous chemicals and providing them with safe operating procedures. Familiarize yourself with the pictograms and proper hazards via OSHA's Quick Card and view the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) of any chemicals you use in your workplace. To keep the conversation going, download the Hazcom Update Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below. Falls in the workplace continue to be the leading cause of fatal accidents accounting for nearly 900 deaths each year. That’s why fall protection for exposed heights 6ft or greater is an important aspect to any safety plan. One of the simplest yet effective fall protection systems that are frequently used are guardrails. Let’s discuss how these systems are designed and why they are effective among leading edges.
Guardrail Design Guardrails are designed with four different components:
Benefits of a Guardrail Some benefits of a guardrail system include:
While there are many ways to protect yourself from falls, guardrails are one of the most economical and effective when faced with leading edges and open hazards. To keep the conversation going, download the Guardrails Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below. With over 280 million cars traveling on 4 million miles of paved roads, accidents are bound to happen. While there are many factors that contribute to the 2 million accidents each year, a Defensive Driver does their best to identify all hazards and be ready to act on them at any moment. Today we will look into what is a Defensive Driver and discuss the most common hazards to prepare for.
What is a Defensive Driver? A defensive driver is someone who uses safe driving techniques to identify road hazards and reduce the risk of an accident. Safe driving techniques include things such as:
Weather Conditions Varying types of weather conditions will affect the way you and your vehicle can respond to hazards. The best way to prepare for weather related hazards is to make sure your vehicle is properly maintained. Having good tire treads, brake pads, windshield wipers, headlights, and window visibility will allow you to brave the elements regardless of rain or snow. Other Vehicles The biggest risk to you on the roadways is other vehicles. While you can’t control others from being distracted or disobeying traffic laws, you can prepare yourself for these types of drivers. Keeping a safe distance between you and other vehicles, allowing enough room to merge or pass, and checking blind spots and mirrors regularly will allow you to identify all surrounding vehicles and move freely as you travel about. Pedestrians Along many roadways there are sidewalks and crosswalks allowing for foot traffic. One thing to always remember when it comes to pedestrians: they have the right of way. You can communicate with them by using your signals, making eye contact, and by coming to complete stops so that they can safely cross intersections and crosswalks. As you hop into your car and prepare for the next road trip, remember that driving requires your undivided attention. Stay alert, use safe driving techniques, and know how to prepare for hazards you may be driving around. To keep the conversation going, download the Distracted Driving Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below. Mobile Elevated Work Platforms (MEWPs) is the new term for all aerial work platforms and lifts as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) updated its A92 standard in 2021. Now all MEWPs are classified in groups with updated design, use, and training standards. Let’s refresh ourselves on what these groups include, along with the changes in each standard.
MEWP Groups Under the new standard, MEWPs are broken down into two groups:
Design Standard (A92.20) With an updated standard comes new safety features for manufacturers. Some of these new features include:
Safe Operation Standard (A92.22) As new designs are implemented, proper operating techniques must be updated to include these changes. The updated operation procedures now include training regarding the alarm sensors, Safe Use Plans for proper MEWP selection, and written Rescue Plans that include rescues from falls and breakdowns at heights. Training Standard (A92.24) ANSI has said that all MEWP training needs to be updated to reflect the group classifications and the operating standards. Alongside the updated training, all operators, supervisors, and maintenance personnel are required to participate in a two-part training that provides theory (written course) and a hands-on evaluation. While ANSI did not specify an expiration of this training, many will continue to utilize a three-year period before a refresher course is required. As this standard pushes forward new safety and training features, the goal of no accidents in the workplace can hopefully be closer to achieved. To keep the conversation going, download the Aerial Lifts Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below. While all falls are preventable, they continue to be the leading cause of fatalities in the workplace. As OSHA continues to put an emphasis on fall prevention, one of the best ways to prevent falls is a Personal Fall Arrest System (PFAS). Let’s take a look at the parts of a PFAS and some of the safety points of use.
PFAS Components OSHA defines a PFAS as a system used to arrest an employee in a fall from a working level. A PFAS system includes an anchor, connector, body harness, and sometimes additional equipment such as lifelines and shock absorbers. Here is the purpose of each component: Anchor Anchor points are where the PFAS begins and acts as the point to suspend the load during a fall. Anchor points are required to be independent from any other type of support. All anchors must be able to support 5,000lbs per employee, maintain a safety factor of two, or designed and installed by a professional. Connector Connectors link the anchor point to the body harness, usually in the form of a lanyard or self-retracting device. Connectors must be fitted with locking snap hooks or d-rings and need to be limited in length so an employee cannot fall to a lower level or more than 6ft. Body Harness A full body harness is the component that helps distribute the impact of the fall to the lower half of the body. Harnesses need to be fitted for each employee and inspected before each use. Any signs of wear, tears, or faulty clips must be reported and the harness removed from use. Additional Equipment Extra equipment such as lifelines can be helpful by increasing the area of work for employees allowing for more movement. Shock absorbers are a common addition to lanyards and lifelines as they reduce fall loads by up to 50%. Safety Points for Use Before using your PFAS, here are some safety tips to remember and follow:
When it comes to PFAS, inspecting equipment before use, limiting the fall distance, and having a plan in place to rescue a fallen worker are just as important to knowing your components and how to use them properly. To keep the conversation going, download the PFAS toolbox talk (TBT) or comment below. While the New Year has officially begun, so does the cold weather for most of us. With dropping temperatures and freezing precipitation comes the risk of Cold Stress as you work outdoors. Let’s take a look at what Cold Stress is and some ways to keep you safe this winter season.
What is Cold Stress? Cold Stress is a condition that occurs when your body is no longer able to maintain its’ normal temperature. As your body temperature begins to drop, symptoms such as shivering, rashes, muscle stiffness, drowsiness, and exhaustion can occur. If these symptoms are not treated quickly, the body will begin to shutdown as you lose consciousness and the situation can turn fatal. Here are some tips to keep your body warm as you work: Acclimate Yourself to the Weather Just like in the hot summer months, acclimating your body to cold weather helps prevent the initial shock of the cold. Build up your tolerance to the cold by slowly introducing yourself in short periods. Wear Proper Clothing The best way to stay warm is to wear layers of loose-fitting clothing. Tight fitting clothes can slow blood flow and reduce the ability to stay warm. Don’t forget to swap clothes as they get wet (especially socks). Stay Hydrated Drink plenty of warm fluids such as water and electrolyte drinks to keep hydrated. Stay away from caffeinated drinks and steer clear of alcohol. Take Breaks Make sure to take breaks throughout the day. When taking a break, try to move to a warm area and allow your body to warm itself up. Stay away from large meals as these can drain your energy. As the cold weather moves in, take these tips and apply them to your workday. To keep the conversation going, download the Cold Stress Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below. While decking the halls for the holidays is fun and exciting, it can turn dangerous in an instant. With over 18,000 Americans taking visits to the ER for holiday related incidents, the most common come from decorating the outdoors with lights and décor. Today we will be reviewing some of the best ways to keep safe while working at heights with lights.
Check Lights and Décor Before Install Make sure all light strings are in working order and replace any worn or frayed cords before climbing a ladder. Being able to use both hands for electrical inspections on the ground will prevent potential electrical hazards and distractions. Inspect Working Area Make sure ladders have proper footing and are free of any ice/snow. Inspect your roof/gutters to make sure there are no spots that cannot handle the weight of you or your decorations. Use Three Points of Contact with Ladders Always maintain three points of contact when moving up and down the ladder. Make sure your hands are free of tools/decorations as you move. Know Your Surroundings When on the Roof Be aware of any snow/ice accumulation along with your electrical cords. Trip and fall hazards are the number one injury at home and at work. Wear Proper Clothing and Footwear Make sure you are dressed for the weather and your footwear has plenty of traction. Fatigue due to the cold can lead to mistakes that can be costly. Christmas lights are an exciting addition to the home and help ring in the holiday the right way. If you are installing your own lights, make sure you know these safety precautions to keep yourself out of the emergency room this year. To keep the conversation going, download NFPA’s Holiday Safety Tips or comment below. OSHA estimates there are over 20,000 eye and face injuries in the workplace each year. While the number may be staggering, an overwhelming majority of these injuries could have been prevented if the proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) was used. Let’s take a look at the OSHA standard and the common types of eye and face protection.
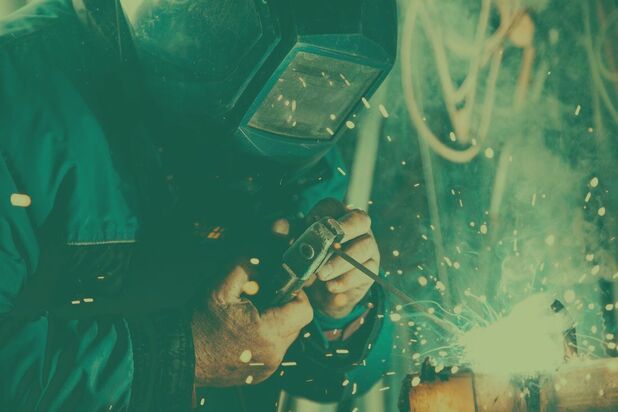
Standard 1910.133 Eye and Face Protection OSHA requires employers to provide protection “when exposed to eye or face hazards from flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation.” Eye & Face Protection is governed by the ANSI Z87.1 Standard where protection must comply based on the different types of hazard ratings including impact, dust, splashes, small particles, and radiation. Each piece of PPE must be marked and easily identified based on the hazards it protects against. While there is no expressed type of PPE for specific tasks, let’s take a look at the most common types of PPE and where they can be used. Safety Glasses The most common type of eye protection that can be used in most construction and manufacturing situations. Safety glasses protect against small hazards from entering the eye and can come with additional side shields to help against flying objects and dust particles. Safety Goggles Providing additional protection to completely cover the eyes, eye sockets, and skin around the eye. Safety goggles are used when additional airborne or liquid hazards are present that may be able to move above or below typical safety glasses. Face Shields Getting the most protection for both the eyes and face. Face shields cover the entire face from forehead to chin, minimizing the potential impact from any types of hazards. Most face shields are impact or chemical rated for protection against large flying objects or acidic/caustic chemicals and gases. Weld Hoods A safety feature designed specifically for protection against radiation. Weld hoods are used with interchangeable filtered lenses to protect against all types of radiant energy from welding and soldering. Before using a weld hood, check the corresponding shade number located on the lens to make sure it is rated for the task at hand. While most people don’t think of Eye and Face Protection as life or death, it can be life threatening as over 1 million workers have lost some degree of sight due to these injuries. Making sure you select the right type of eye and face protection and wearing it properly can significantly reduce your risk of injury. To keep the conversation going, download our Eye & Face Toolbox Talk (TBT) or comment below. OSHA estimates there are 200 workplace fires each day. With over $2 billion annually in property damage from these fires, it is important that work involving sparks and flammable materials be conducted under close supervision. Let’s look at Hot Work Permits and what your responsibilities are during these activities.
Hot Work is defined as operations that can create a spark or flame. In most cases this involves welding, cutting, brazing, and soldering. Permits for this type of work is required by OSHA and should contain the following:
Hot Work Precautions Depending on the location and type of work, additional rules should be followed when performing hot work activities. Some of these rules include:
Fire Watch Duties When tasked as the designated Fire Watch, the employee will be required to focus solely on watch duties. These duties include:
Hot Work is an everyday task that can go from safe to serious very quickly. Understanding the precautions and duties during these permits will ensure employees and the jobsite will be safe from fires. To keep the conversation going, download the Hot Work Permits Toolbox Talk (TBT). |
AuthorSTAC Admin Categories
All
Archives
July 2024
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed