|
OSHA Standard: 1926.300 – Subpart I – Tools – Hand & Power Training: Training should be performed upon initial assignment/before use of tool. Frequency: When roles, conditions, or equipment changes. Or when worker is using the equipment in an unsafe manner. Background:
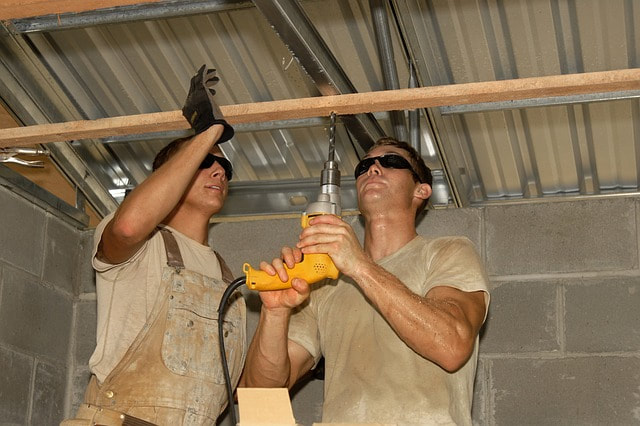
Employees using electric tools must be aware of several dangers. Among the most serious hazards are electrical burns and shocks. Electrical shocks, which can lead to injuries such as heart failure and burns, are among the major hazards associated with electric powered tools. Under certain conditions, even a small amount of electric current can result in fibrillation of the heart and death. An electric shock also can cause the user to fall off a ladder or other elevated work surface and be injured due to the fall. To protect the user from shock and burns, electric tools must have a three-wire cord with a ground and be plugged into a grounded receptacle, be double insulated, or be powered by a low-voltage isolation transformer. Three-wire cords contain two current carrying conductors and a grounding conductor. Any time an adapter is used to accommodate a two-hole receptacle, the adapter wire must be attached to a known ground. The third prong must never be removed from the plug. Double-insulated tools are available that provide protection against electrical shock without third-wire grounding. On double-insulated tools, an internal layer of protective insulation completely isolates the external housing of the tool. Employer Requirements: The employer is responsible for the safe condition of tools and equipment used by employees. Employers shall not issue or permit the use of unsafe tools. Employees should be trained in the proper use and handling of tools and equipment. Appropriate personal protective equipment such as safety goggles and gloves must be worn to protect against hazards that may be encountered while using hand tools. Employee Requirements: To prevent hazards associated with the use of power tools, workers should observe the following general precautions:
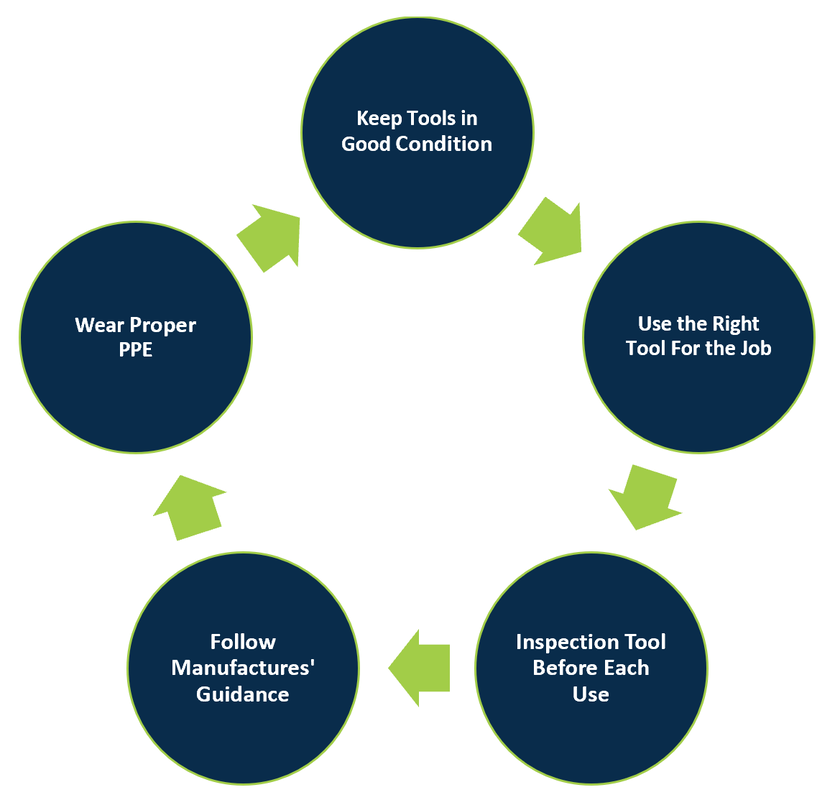
Take Home Points: Both employer and employee have responsibility in ensuring safety while operating tools. Ensure that the tool is maintained and inspected, use the right tool for the right job, follow manufacturers’ guidelines, ensure the workplace is safe for use of the tool, and wear the appropriate PPE.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSTAC Admin Categories
All
Archives
July 2024
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed